Our Views
Stakeholder Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide
In the development industry, when executing consultancy assignments, it's very common to face the need of conducting a Stakeholder Analysis. This process is not just about mapping interests; it's about forging pathways to sustainable impact by understanding and aligning with the diverse array of stakeholders involved in development projects.
Whether it’s infrastructural development, policy reform, or community empowerment initiatives, the success of these projects hinges on the ability to navigate complex stakeholder landscapes.
This article will help you meet and exceed the expectations of your clients, partners and beneficiaries in the process of stakeholder analysis.
Join us as we explore the critical steps for conducting a meaningful stakeholder analysis, highlight the significance of this process in the development sector, and share expert tools and techniques for mastering stakeholder engagement. Whether you're a novice stepping into the world of development consultancy or a seasoned expert seeking to refine your approach, this guide offers valuable insights tailored to enhance your impact in the field of development.
What is a Stakeholder Analysis?
Definition of Stakeholder Analysis
Stakeholder Analysis is a systematic approach used to identify, evaluate, and prioritize the individuals or groups that have an interest in, or influence on, a project or policy, particularly within the context of development consultancy. It is a foundational step in project planning and management, ensuring that the needs, expectations, and potential impacts on stakeholders are carefully considered from the outset.
In the development sector, where projects often aim to address complex social, economic, and environmental challenges, understanding the stakeholder landscape is crucial. Stakeholders in these contexts can range from local communities, government bodies, and civil society organizations to international donors, NGOs, and private sector partners. Each brings unique perspectives, interests, and levels of influence that can significantly affect a project's trajectory and outcomes.
What is the purpose of a Stakeholder Analysis?
The primary objective of stakeholder analysis is to develop a strategic understanding of:
- Who the stakeholders are: Identifying all potential individuals or groups affected by or interested in the project.
- Their interests and how they might be affected: Understanding stakeholders' needs, concerns, and how the project could impact them.
- Their influence and power: Assessing the level of influence and power stakeholders have over the project's success or failure.
- Strategies for engagement: Based on the analysis, determining how best to engage each stakeholder group to foster support, mitigate resistance, and ensure sustainable project outcomes.
This process involves several steps, including mapping stakeholders, assessing their interests and influences, and planning engagement strategies. By conducting a thorough stakeholder analysis, development consultants can gain invaluable insights into the project ecosystem, enabling them to make informed decisions, anticipate challenges, and build robust strategies for stakeholder engagement.
Effective stakeholder analysis not only facilitates smoother project implementation but also enhances the legitimacy and sustainability of development initiatives. It ensures that projects are responsive to the needs of those they aim to serve, while also aligning with the goals of funding agencies and partners. Ultimately, stakeholder analysis is about building bridges between diverse groups, fostering collaboration, and ensuring that development projects achieve their intended impact, benefiting all parties involved.
Advantages and benefits of a Stakeholder analysis in project management
Stakeholder Analysis plays a pivotal role in the success of project management, especially within the dynamic and multifaceted landscape of development consultancy. By systematically identifying and evaluating the interests and influences of various stakeholder groups, projects can be designed and implemented in a way that maximizes benefits while minimizing challenges. Here, we delve into the key advantages and benefits of conducting a stakeholder analysis in project management:
Enhanced Strategic Planning
Stakeholder analysis provides crucial insights that feed into strategic planning. It helps project managers and consultants understand the broader environment in which the project operates, highlighting potential support or resistance. This awareness allows for the formulation of strategies that can leverage stakeholder strengths and mitigate risks associated with stakeholder opposition, ensuring a more resilient and adaptable project plan.
Improved Communication and Engagement
Understanding the needs, expectations, and communication preferences of different stakeholders enables the development of tailored engagement strategies. This ensures that communication is effective, relevant, and timely, fostering positive relationships and building trust between the project team and its stakeholders. Effective communication is key to securing stakeholder buy-in and support, which are essential for smooth project execution and adoption.
Risk Identification and Management
Stakeholder analysis helps in early identification of potential risks and challenges that could impede project success. By recognizing the concerns and objections of stakeholders at an early stage, project managers can devise mitigation strategies, prepare contingencies, and engage proactively with stakeholders to address their issues. This proactive approach to risk management contributes to project stability and success.
Enhanced Decision-making
Incorporating stakeholder perspectives into decision-making processes ensures that decisions are well-informed and consider the diverse impacts on various stakeholder groups. This inclusivity can lead to more sustainable and accepted solutions, as decisions are made with a comprehensive understanding of the stakeholder landscape, including potential social, economic, and environmental impacts.
Increased Project Sustainability and Impact
Projects that are aligned with stakeholder interests and needs are more likely to be sustainable in the long term. Stakeholder analysis ensures that projects are not only designed to meet immediate objectives but also contribute to broader, long-term benefits for all stakeholders involved. This alignment increases the likelihood of project success, enhances its impact, and contributes to positive development outcomes.
Building Strong Relationships and Partnerships
A thorough stakeholder analysis fosters stronger relationships and partnerships by identifying opportunities for collaboration and mutual benefit. Engaging stakeholders as partners in the project's design and implementation can enhance resource sharing, innovation, and commitment across the project lifecycle, leading to more robust and impactful outcomes.
How to do a Stakeholder Analysis
Conducting a stakeholder analysis is a strategic process that involves several key steps. Each step is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the stakeholders, their interests, and their potential impact on a project. Here's a step-by-step guide to effectively conducting a stakeholder analysis, particularly within the context of development consultancy projects.
Step 1: Identify Stakeholders
Start by listing all potential stakeholders related to the project. This includes anyone who can affect or be affected by the project’s outcomes. In the development sector, stakeholders can range from local community members, government agencies, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) to international donors, private sector partners, and civil society organizations. Use project documents, brainstorming sessions, and consultations with project team members to ensure a comprehensive list.
Step 2: Analyze Stakeholder Characteristics
Once stakeholders are identified, analyze their characteristics. This involves understanding their interests, concerns, expectations, and the extent to which the project impacts them. Additionally, assess their level of influence and power over the project. Tools such as stakeholder maps or matrices can be helpful in visualizing the relationships between the project and its stakeholders.
Step 3: Prioritize Stakeholders
Not all stakeholders will have the same level of importance or influence on your project. Prioritize them based on their interest and power. A common approach is to use a prioritization matrix, categorizing stakeholders into groups such as high power/high interest, high power/low interest, low power/high interest, and low power/low interest. This helps in focusing engagement strategies where they are most needed.
Step 4: Develop Engagement Strategies
For each stakeholder or stakeholder group, develop tailored engagement strategies. Consider the best ways to communicate with them, involve them in the project, and address their needs and concerns. Strategies can range from regular information updates to direct involvement in decision-making processes. The goal is to ensure stakeholders are appropriately engaged and supportive of the project.
Step 5: Implement Engagement Plans
With strategies in place, implement your stakeholder engagement plans. This may involve setting up meetings, workshops, consultations, or communication campaigns. It's important to be flexible and responsive to stakeholder feedback, adapting your approach as necessary to maintain positive relationships and project support.
Step 6: Monitor and Adapt
Stakeholder analysis is not a one-time task but an ongoing process throughout the project lifecycle. Regularly monitor stakeholder attitudes, interests, and the effectiveness of engagement strategies. Be prepared to adapt your approach based on changing conditions or feedback. This ensures that stakeholder analysis remains a dynamic and integral part of project management.
Stakeholder Analysis Tools and Techniques
Stakeholder analysis may employ various tools and techniques to identify, understand, and engage stakeholders effectively. These methods facilitate a deeper insight into stakeholder dynamics and help in crafting tailored engagement strategies. Below, we explore some of the most widely used tools and techniques in stakeholder analysis, particularly valuable in the context of development consultancy.
Stakeholder Mapping
Stakeholder mapping is a visual tool used to categorize stakeholders based on their level of influence and interest regarding the project. This technique involves creating a two-dimensional matrix where one axis represents the interest of the stakeholders in the project outcomes, and the other represents their power to influence the project. Stakeholders are then plotted on the matrix, helping project managers to prioritize engagement efforts.
Power-Interest Grid
Closely related to stakeholder mapping, the Power-Interest Grid is a specific form of mapping that categorizes stakeholders into four quadrants: high power/high interest, high power/low interest, low power/high interest, and low power/low interest. This grid is instrumental in determining the level of attention each stakeholder or stakeholder group requires, guiding the allocation of resources for stakeholder engagement.
Stakeholder Influence Network Diagrams
These diagrams help identify the relationships between different stakeholders and how they influence each other. By understanding these networks, project managers can identify key influencers and opinion leaders within stakeholder groups. Leveraging these relationships can be crucial in gaining support or mitigating opposition for the project.
Stakeholder Interviews and Surveys
Direct engagement with stakeholders through interviews and surveys is a powerful technique for gathering insights into their perceptions, interests, and concerns regarding the project. This qualitative data is invaluable for developing engagement strategies that are responsive to stakeholder needs and expectations.
Engagement Planning Tools
Tools such as Gantt charts, project management software, and engagement matrices can help in planning, executing, and monitoring stakeholder engagement activities. These tools enable project managers to track progress, ensure timely communication, and adjust strategies based on stakeholder feedback.
Social Network Analysis (SNA)
SNA is a more complex tool that analyzes the social relationships among stakeholders. It can reveal how information flows within networks, identify central figures, and assess the impact of these networks on project outcomes. SNA is particularly useful in large-scale projects with numerous stakeholders and complex interdependencies.
Stakeholder Analysis - Example
Aninver was hired to develop a Stakeholder analysis for the West Africa Coastal Erosion (WACA) Project. The assignment was financed by the Nordic Development Fund and by the West Africa Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU).
The WACA Project focuses on capacity development and improving information and knowledge about climate change related coastal erosion. Our consultancy assingment aimed to promote sound coastal management practices for a select group of countries including Benin, Cote d’Ivoire, Togo and Ghana.
The stakeholders of the WACA project included all key actors at the national and regional levels, i.e. politicians, decision makers, technical and operational staff, private sector, affected populations, civil society, academia, media, etc.
To execute the stakeholder analysis, the consultants undertook an initial desk study of existing material and conducted interviews (in person or virtually) with key stakeholders in each country in order to prepare each of the four stakeholder analysis.
Later, the team used a Stakeholder mapping to categorize stakeholders based on their level of influence and interest regarding the project.
As a result, our team of consultants prepared an analysis on the identification of opportunities and challenges for private sector participation in coastal areas development and management.
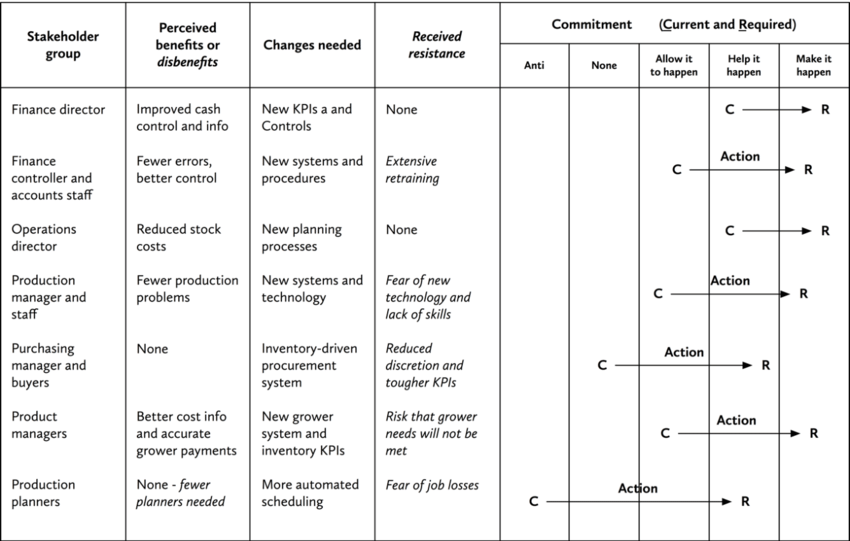
Stakeholder analysis Template
A stakeholder analysis template is a framework that provides a structured approach for identifying and assessing the impact of individuals or groups on a project. This template is designed to facilitate the systematic examination of stakeholders and their potential influence, which is crucial for developing effective engagement strategies. Check out the template below:
Conclusion
Stakeholder analysis stands as a fundamental pillar, particularly within the world of development consultancy. The process goes beyond merely identifying who the stakeholders are; it delves into understanding their interests, assessing their influence, and developing tailored strategies for engagement that align with project goals. The real-world examples highlighted in this guide illustrate the transformative power of stakeholder analysis in navigating complex project landscapes, fostering collaboration, and enhancing project outcomes.
As we have seen, the strategic application of stakeholder analysis is essential for anyone involved in project management within the development sector. It is a critical step towards achieving project objectives that are not only successful in the short term but also sustainable and beneficial in the long run. As development consultants and project managers, embracing the practice of stakeholder analysis is embracing a path towards more impactful, inclusive, and successful projects.
Let this guide serve as a starting point for your journey in mastering stakeholder analysis. Whether you are new to the field or looking to refine your approach, remember that the success of your projects lies in the value you place on understanding and engaging with your stakeholders. Through thoughtful analysis and strategic engagement, we can all contribute to creating development outcomes that are truly transformative.










